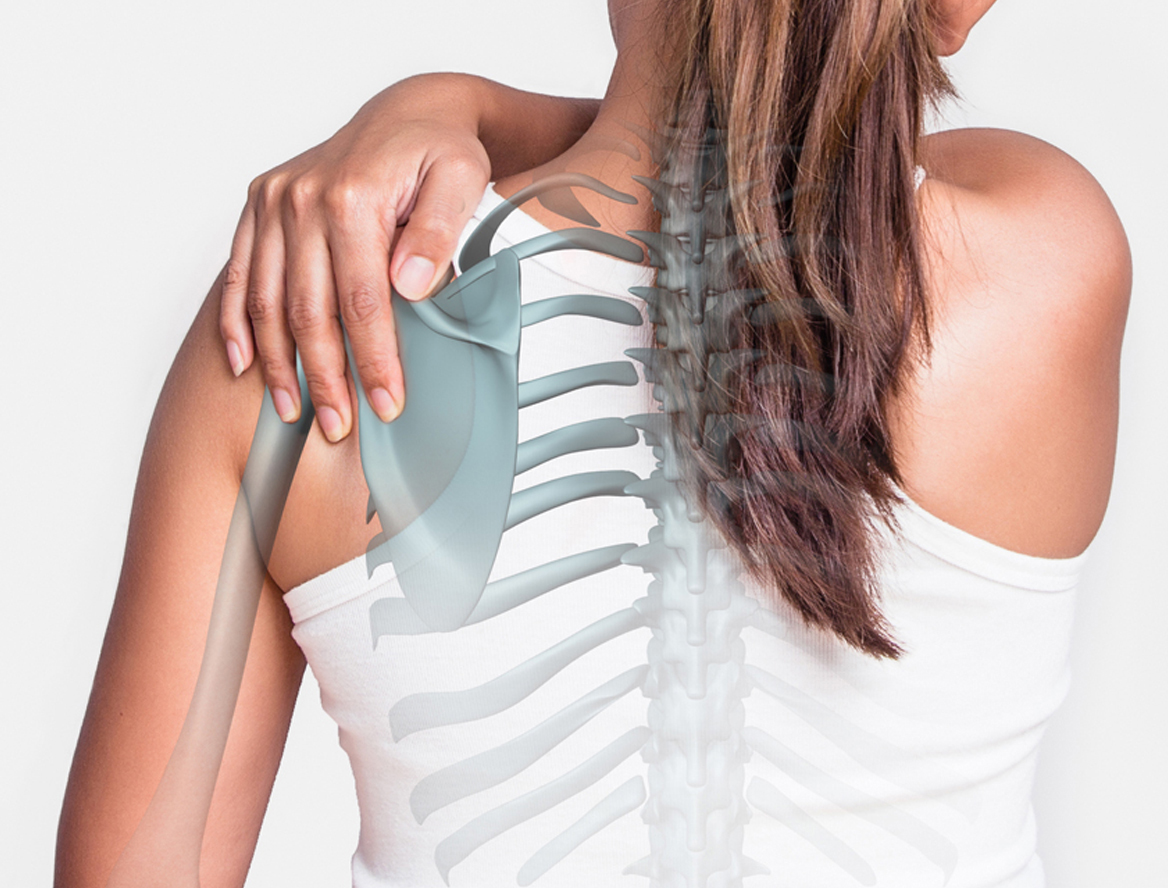
Orthopaedic Evaluation
Your family physician may refer you to an orthopaedic surgeon for a thorough evaluation to determine if you can benefit from this surgery.
An evaluation with an orthopaedic surgeon consists of several components:
- A Medical History: Your orthopaedic surgeon will gather information about your general health and ask you about the extent of your shoulder pain and your ability to function.
- A Physical Examination: This will assess shoulder motion, stability, and strength.
- X-Rays: These images help to determine the extent of damage in your shoulder. They can show loss of the normal joint space between bones, flattening or irregularity in the shape of the bone, bone spurs, and loose pieces of cartilage or bone that may be floating inside the joint.
- Other Tests: Occasionally blood tests, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, or a bone scan may be needed to determine the condition of the bone and soft tissues of your shoulder.
Orthopaedic surgeon will review the results of your evaluation with you and discuss whether shoulder joint replacement is the best method to relieve your pain and improve your function. Other treatment options — including medications, injections, physical therapy, or other types of surgery — will also be discussed and considered.
Complications
Your orthopaedic surgeon will explain the potential risks and complications of shoulder joint replacement, including those related to the surgery itself and those that can occur over time after your surgery.
When complications occur, most are successfully treatable. Possible complications include the following.
- Infection
- Prosthesis Problems
- Nerve Injury
Do’s and Don’ts
The success of your surgery will depend largely on how well you follow your orthopaedic surgeon’s instructions at home during the first few weeks after surgery. Here are some common do’s and don’ts for when you return home:
- Don’t use the arm to push yourself up in bed or from a chair because this requires forceful contraction of muscles.
- Do follow the program of home exercises prescribed for you. You may need to do the exercises 2 to 3 times a day for a month or more.
- Don’t overdo it! If your shoulder pain was severe before the surgery, the experience of pain-free motion may lull you into thinking that you can do more than is prescribed. Early overuse of the shoulder may result in severe limitations in motion.
- Don’t lift anything heavier than a glass of water for the first 2 to 4 weeks after surgery.
- Do ask for assistance. Your physician may be able to recommend an agency or facility if you do not have home support.
- Don’t participate in contact sports or do any repetitive heavy lifting after your shoulder replacement.
- Do avoid placing your arm in any extreme position, such as straight out to the side or behind your body for the first 6 weeks after surgery.
ELBOW REPLACEMENT:
During elbow replacement, a surgeon replaces your elbow with an artificial joint made from two implants that attach to the bones in your arm. A metal and plastic hinge joins the implants together. The procedure is similar to hip and knee replacements.
If a disease such as rheumatoid arthritis or an injury has harmed your elbow, doctor may recommend surgery to replace the joint, so you have less pain and can move better.
During elbow replacement, a surgeon replaces your elbow with an artificial joint made from two implants that attach to the bones in your arm. A metal and plastic hinge joins the implants together.
Elbow replacement usually reduces pain and helps your elbow work better. But it may not make the joint as good as it was before disease or injury hurt it.
You’ll need to avoid activities that can cause further injury, such as hammering, playing contact sports, and lifting heavy weights. With good care, your new elbow should serve you well for many years.
Risks & Complications Associated:
The most common complications and risks associated are:
- Infection
- Injury to nerves and blood vessels
- Allergic reaction to the artificial joint
- Broken bone
- Stiffness or instability of the joint
- Loosening or wearing of the artificial parts
- Weakness or failure in the tendons of your arm
- Pain There are risks because of the anesthesia, such as an allergic reaction to those medicines and breathing problems. As with any surgery, bleeding and blood clots are possible, too.